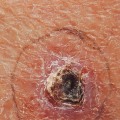
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a type of skin cancer that can be life-threatening if not treated in time. It is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms of SCC and to get regular skin checks from a dermatologist. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for successful outcomes. SCC is caused by damage to the skin cells, usually from exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
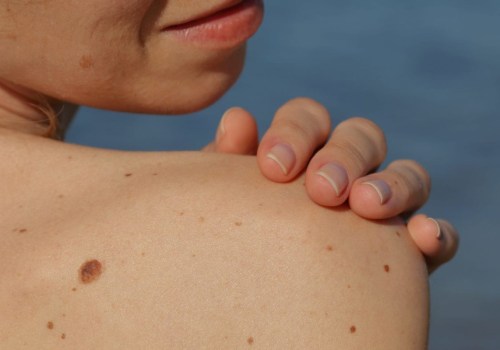
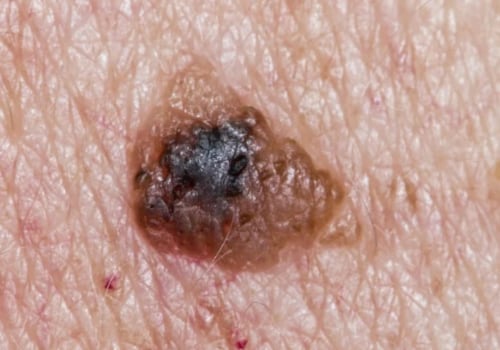
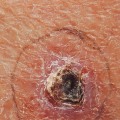
It can also be caused by other factors such as smoking, radiation therapy, and certain chemicals. SCC usually appears as a firm, red nodule or a flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface. It may also look like a sore that doesn’t heal or an area of thickened skin. If you notice any changes in your skin, it’s important to see a dermatologist right away.
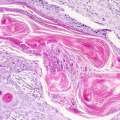
Your doctor will examine your skin and may take a biopsy of the suspicious area. A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope. This is the only way to definitively diagnose SCC. Your doctor may also order imaging tests such as an X-ray or CT scan to check for signs of cancer spread beyond the skin.
If you are diagnosed with SCC, your doctor will discuss treatment options with you. Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. The type of treatment will depend on the size and location of the tumor, as well as other factors such as your age and overall health. It’s important to take steps to reduce your risk of developing SCC.
Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher when outdoors and avoid tanning beds. Wear protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts and wide-brimmed hats when outdoors. And if you smoke, quit!.