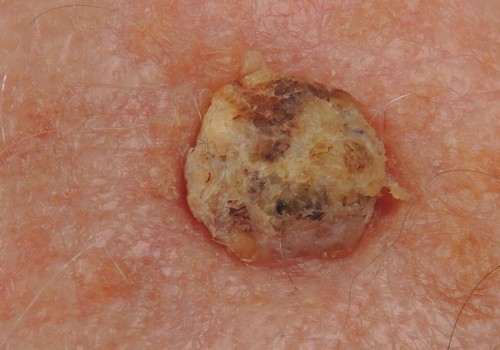
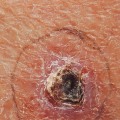
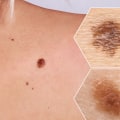
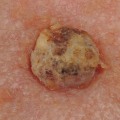
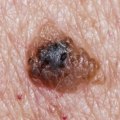
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a type of skin cancer that affects the outermost layer of the skin. It is one of the most common forms of skin cancer, and it can be found in both men and women. SCC is caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds, as well as certain types of HPV. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of SCC so that it can be treated as soon as possible.
SCC usually appears as a firm, red nodule or a flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface. It may also present as an open sore that bleeds or develops a crust. The lesion may be tender to the touch and may grow quickly. In some cases, SCC may spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes or other organs.
The diagnosis of SCC is made through a biopsy, which involves taking a sample of the affected tissue and examining it under a microscope. Treatment for SCC depends on the size and location of the tumor, as well as whether it has spread to other parts of the body. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. It is essential to take steps to reduce your risk of developing SCC.
This includes avoiding direct sun exposure during peak hours (10am-4pm), wearing protective clothing and sunscreen when outdoors, avoiding tanning beds, and getting regular skin checks from your doctor.