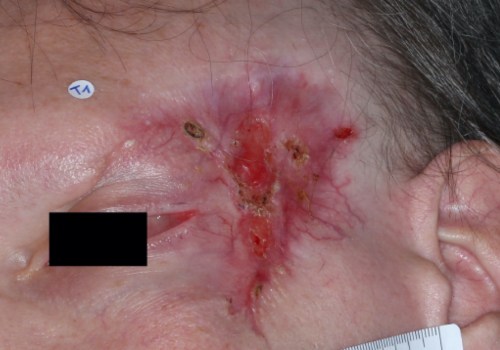
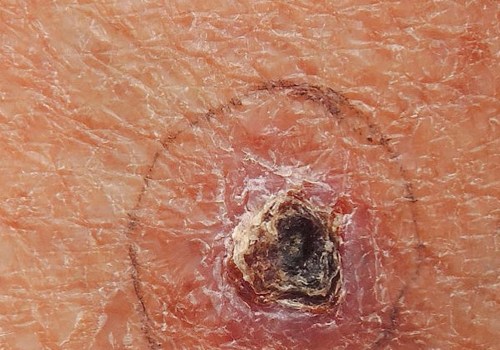
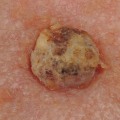
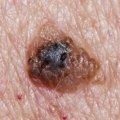
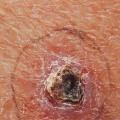
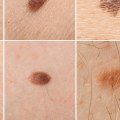
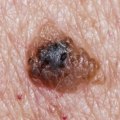
Skin cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer, and it is essential to be aware of the risk factors associated with it. While some of these factors are out of our control, such as age and family history, there are other elements that can be managed to reduce the risk of developing skin cancer. The most common type of skin cancer is basal cell carcinoma, which is caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can cause skin cancer.
The likelihood of developing skin cancer increases with age, and people with fair skin, light hair, and blue eyes are more prone to it. Those who have had severe sunburns in the past are also at a higher risk. Other risk factors for skin cancer include a weakened immune system, exposure to certain chemicals such as arsenic, and a family history of skin cancer. People who have had organ transplants or take medications that suppress the immune system are more likely to develop skin cancer.
Additionally, those who work outdoors or spend a lot of time in the sun are more likely to develop skin cancer. It is important to take steps to reduce your risk of developing skin cancer. Wearing sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and wearing protective clothing when outdoors can help protect your skin from UV radiation. Avoiding tanning beds and limiting your time in the sun can also help reduce your risk.
Additionally, it is important to check your skin regularly for any changes in moles or other spots that could be signs of skin cancer. By understanding the risk factors for skin cancer and taking steps to reduce your risk, you can help protect yourself from this potentially deadly disease. If you have any concerns about your risk for skin cancer, talk to your doctor about ways you can reduce your risk.