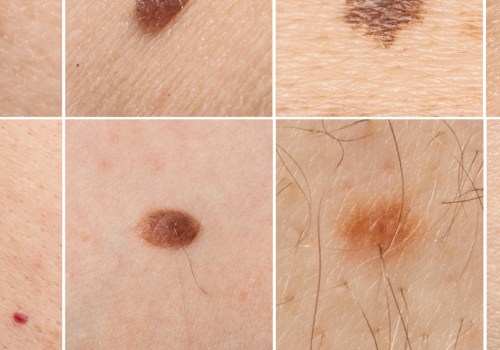
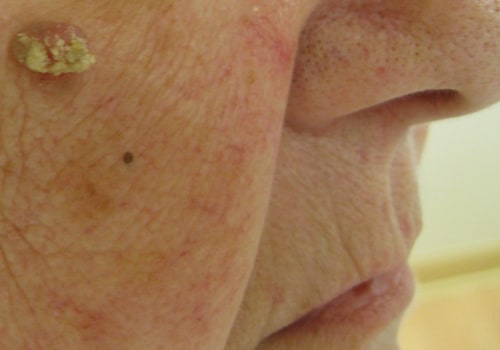
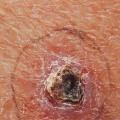
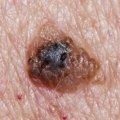
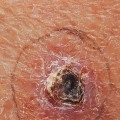
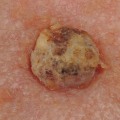
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a type of skin cancer that affects the outermost layer of the skin. It is one of the most common forms of skin cancer, and it can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Knowing the risk factors associated with SCC can help you take steps to reduce your risk and protect your health. The most important risk factor for SCC is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, which can lead to mutations that cause cancer. People who spend a lot of time in the sun or use tanning beds are at an increased risk for SCC. Other risk factors include having fair skin, a family history of skin cancer, and having certain medical conditions such as HIV or organ transplantation. People who have had skin cancer before are also at an increased risk for developing SCC.
This is because they have already been exposed to UV radiation and their skin cells may have already been damaged. Additionally, people who have had radiation therapy for other types of cancer may be at an increased risk for SCC. Certain medications can also increase your risk for SCC. These include immunosuppressant drugs used to treat autoimmune diseases, such as psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as drugs used to treat organ transplant rejection.
Additionally, some chemotherapy drugs used to treat other types of cancer can increase your risk for SCC. Smoking is another risk factor for SCC. Smoking damages the DNA in skin cells, which can lead to mutations that cause cancer. Additionally, smoking can weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off cancer cells.
Finally, certain types of HPV (human papillomavirus) can increase your risk for SCC. HPV is a sexually transmitted virus that can cause warts and other types of skin lesions. Some types of HPV are linked to an increased risk for SCC. If you are concerned about your risk for SCC, talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk.
Limiting your exposure to UV radiation is one of the best ways to reduce your risk. Wearing sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher when you are outside and avoiding tanning beds can help protect your skin from UV damage. Additionally, quitting smoking and avoiding certain medications can help reduce your risk. Finally, practicing safe sex and getting vaccinated against HPV can help protect you from this virus and reduce your risk for SCC.